As our technology and lifestyle choices continue to become smarter and more advanced, by comparison, the batteries that power our progress don’t seem to have evolved at all… or have they?
The battery, by definition, is a device that converts chemical energy directly into electrical energy. It captures energy produced at one time and stores it for use at a later time.
This concept has been around for a lot longer than you might think.
The Past
In 1938, in the basement of The Baghdad Museum, the director found what is now known as the controversial ‘Baghdad Battery’. It is also referred to as the Parthian battery. Twelve were found in total, each with the capability of generating between 1.5 and 2 volts of electrical energy. This is the energy equivalent of a modern AA battery (which provides approximately 1.5 volts). They were believed to have been of Mesopotamian origin and were dated at around 150 BC to 223 AD.
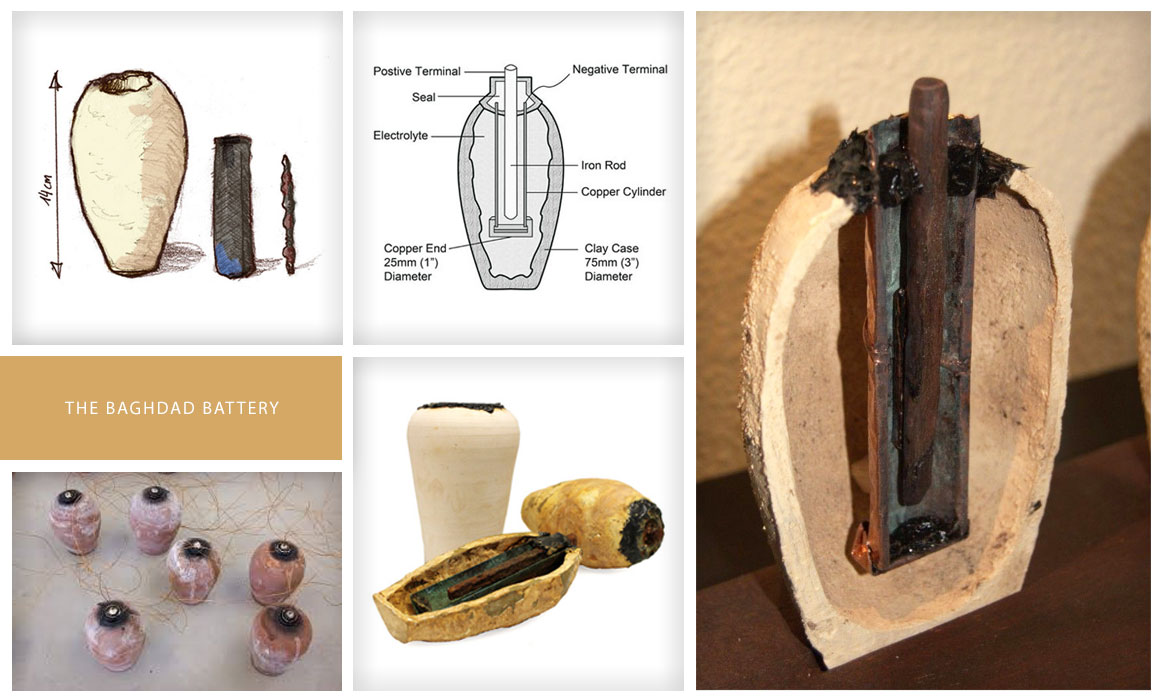

As there is only speculation as to the purpose of these ancient devices, it is impossible to prove that they were ever utilised as energy stores or batteries as we know them.
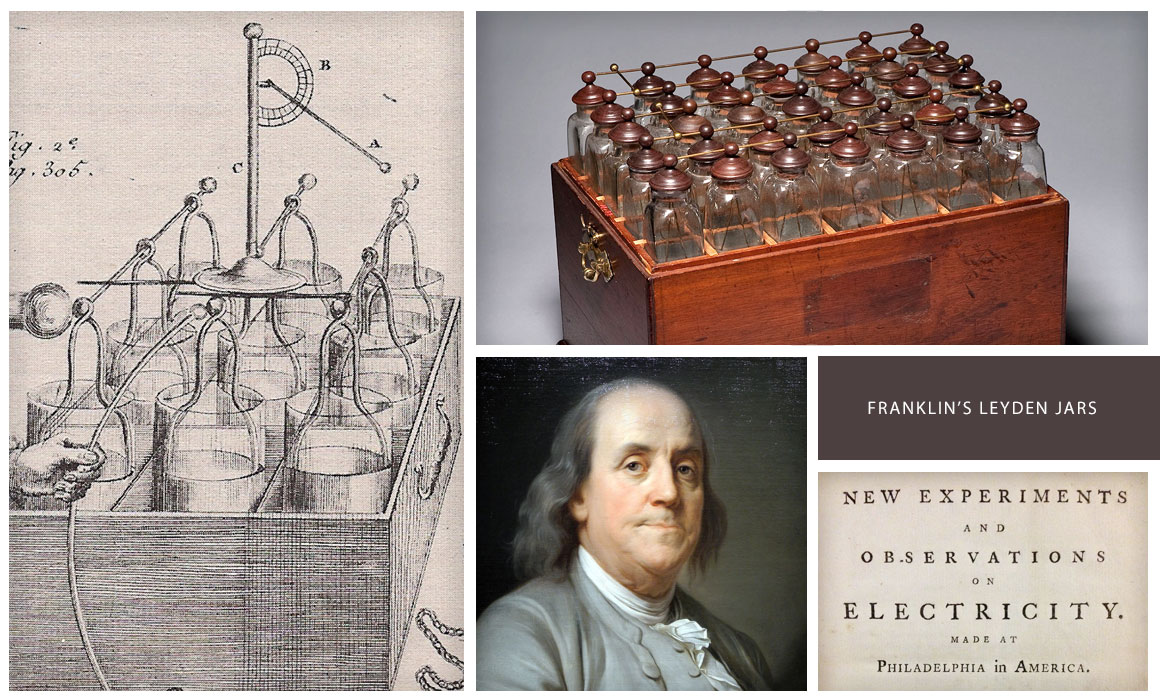
The word ‘battery’, is believed to be first used in the late 1740’s by American scientist and inventor Benjamin Franklin. He used it to describe a set of linked glass capacitors (Leyden Jars) while experimenting with electricity.
The first known truly functional battery was invented in 1800 by the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta. He used stacked discs of copper and zinc, separated by a cloth soaked in a saltwater solution, to produce a continuously stable current.
The lead-acid rechargeable battery was invented in 1859. It is still used to start most internal combustion engine cars today.
The Present
More recently, lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries have become the go-to power source for just about every imaginable device. A vast majority of our homes, phones, and cars are powered this way.
For homeowners with solar panels, Li-ion systems may allow them to store the energy they produced even after the sun has gone down. This helps them to avoid paying higher electricity rates. Although Li-ion solutions can pack a lot of power in a relatively small space and hold a charge extremely well, they do have a ‘dark side’. If you can excuse the irony – there are plenty of negatives to all the positives.

Experts believe that currently less than 5% of Li-ion batteries are recycled. Although generally speaking they are quite safe, there has been cause for concern. There have been incidents of overheating, causing fires and in some cases even exploding. As a safety precaution, the FAA recently announced that these batteries would no longer be allowed in checked baggage. Every single type of Li-ion battery – from those in home solar storage to those in portable devices require cobalt in the manufacturing process. There are also many reports of shocking labour abuses linked to cobalt mining, including exploitation, cruelty, slavery and child labour.
This week, Core Architects met with leaders of the German industry on energy-efficient systems to learn about new technologies for energy storage.
The Future
The Solar-Hydrogen Revolution
We are on the verge of another giant leap. The future of batteries and energy storage could well belong to solar-hydrogen systems. With these systems, hydrogen and oxygen are produced via solar power and then stored to produce electricity when no sunlight is available.
Some see hydrogen gas as the ‘clean fuel’ of the future. It is generated from water and returns to water when it is oxidised.
Hydrogen-powered fuel cells are increasingly being seen as ‘pollution-free’ sources of energy. They are now being used more and more in bus and car production.
The world’s first fully off-grid energy sufficient housing complex is currently being realized in the Vårgårda municipality of Sweden. The entire complex will be powered by combining solar PV and hydrogen fuel cells. Once completed, all six apartment blocks (172 flats) will have all their electricity and heating needs met through the on-site solar generation and storage solution. Any excess energy is stored for later use.
The so-called ‘Hydrogen House’ in New Jersey has been entirely self-powered since October 2006. It runs purely on electricity generated from the sun and stored hydrogen.
These example dwellings are 100% off grid, sustainable and environmentally friendly – the only by-product being water vapour.
Energy storage and battery technology have come a long way since 150 BC.
The future is indeed bright and as we have learned this week… not as far away as you might think!


